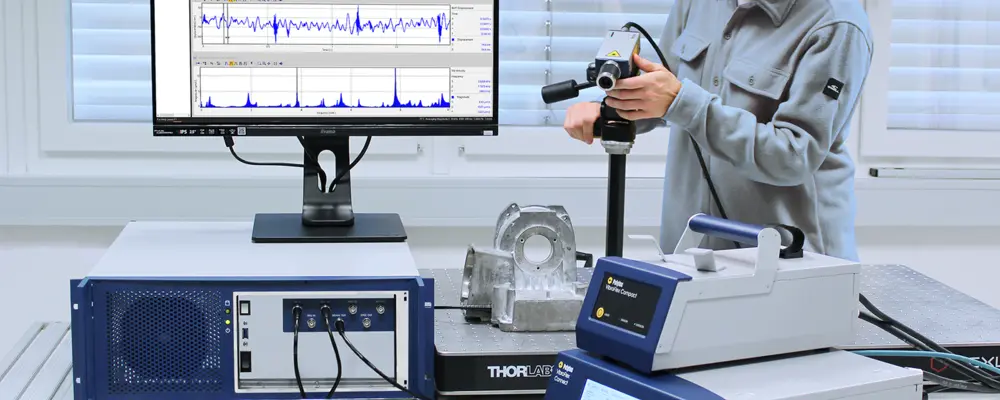
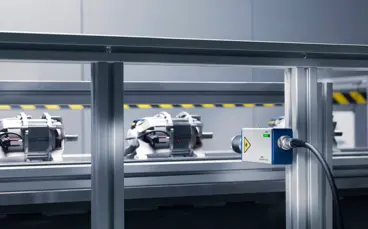
Resonance testing for quality control
Resonance testing is a valuable technique used in various industries to assess the structural integrity and quality of mechanical components or systems by analyzing their natural vibration frequencies and modes. It involves exciting the component with a mechanical or acoustic force or input and then measuring the response of the component to determine its resonance characteristics. Resonance testing describes the analysis of resonances of a sample by characterizing its vibrational signature. In industrial manufacturing, the resonant inspection often as an end-of-line test, allows clear pass-fail decisions, detecting defects for excluding maleficient parts from production lines.
Optical vibraiton sensors like laser Doppler vibrometers provide a non-contact, high precision alternative measurement solution for determining the resonance frequency, resulting in many advantages in the context of acoustic resonance testing.
Polytec Magazine
Measuring acoustic signatures and testing resonances at production level
Measuring the resonance frequency from DC to MHz and GHz
Typical phases and steps in resonance testing
Resonance analysis typically includes the following steps:
- Excitation: A force or input signal is applied to the component under test. This input can be mechanical, such as a shaker or hammer strike, or acoustic, such as a sound wave. The goal is to excite the component at a range of frequencies to identify its natural resonance frequencies.
- Measurement: Sensors are placed at various points on the component to measure its response to the excitation. These sensors record data, such as displacement, velocity, or acceleration, which is crucial for the subsequent analysis.
- Data Analysis: The collected data is then analyzed to identify the resonance frequencies or mode shapes of the component. Resonance frequencies are the frequencies at which the component vibrates most strongly, indicating potential structural weaknesses and defects, providing information about material propoerties and health status.
- Interpretation: Engineers interpret the resonance data to assess the health and quality of the component. Any deviations from expected resonance frequencies or unusual mode shapes can indicate defects, fatigue, or other structural issues that may compromise the component's performance or safety.

Optical, non-contact resonance testing using laser sensors
Resonance analysis seeks to identify the natural frequencies or resonant modes of an object. When an object is subjected to vibrations at or near its natural frequencies, it tends to vibrate with larger amplitudes. This effect allows for detecting structural issues, defects, or weaknesses. By analyzing the frequency response, engineers can gain insights into the structural characteristics of the object being tested, including its stiffness and mechanical properties, damping properties and overall integrity.
Laser Doppler vibration measurement is an advanced optical technology that offers several advantages in the context of resonance testing:
- High precision: Laser-based measurement systems provide extremely accurate and precise data, enabling engineers to detect even subtle changes in an object's vibrational behavior.
- Non-contact: Laser vibrometers do not physically touch the object being tested, minimizing interference and ensuring that measurements do not alter the object's properties. This is crucial when testing delicate and sensitive components or even hot objects where sensors cannot be applied.
- Wide frequency range: Laser vibrometers can measure a wide range of frequencies, making them suitable for low-frequency up to high-frequency (GHz) resonance analysis.
- Remote sensing: Laser vibrometers can be used to measure vibrations from a distance, allowing engineers to assess components in situ without the need for direct physical access. This is indispensable in danger zones like high voltage or explosive areas.
- Rapid data acquisition: Laser vibrometers can capture data quickly with both analog and digital data transfer, thus enabling real-time analysis and immediate feedback during testing.





Optical metrology and laser sensors for resonance measurement
Become an expert: tips, tricks & video tutorials
The IVS-500 Industrial Vibration Sensor from Polytec is a dedicated and flexible measuring device for the vibroacoustic end-of-line test. This exclusive section (login) presents the basics of optical resonance testing using laser vibrometers including a technology benchmark for resonance testing and valuable tips & tricks video tutorials for the use and handling of the IVS-500 Industrial Vibration Sensor - for starters, current users, integrators and testing experts.
Testing resonances of hard disk drives and precision parts
As a case study, hard disk drives – with their ever growing storage densities and shorter access times – require extremely high levels of stability as regards the read/write head’s location and positioning in relation to the disk drive interface. The flying height is a compromise between competing effects. A lower flying height enables better local resolution for read/write operations and thus a higher data density; meanwhile the risk of collisions with the medium grows at the same time. The flying height is just a few nanometers and very much depends on the ambient pressure due to the aerodynamic bearing. The aerodynamic bearing, however, has resonances that depend on the ambient pressure too and that may lead to instabilities.
Since the measurement process is both non-contact and non-intrusive, in this situation using laser vibrometers is the only way of measuring the response behaviour of the read/write head including its suspension following dynamic excitation. When performing resonance test measurements with single-point and scanning vibrometers, the frequency spectrum of the read/write head’s deflection is measured as a function of the ambient pressure. You can use this to identify critical conditions and then make constructive changes. The goal of the optimization process is to develop read/write units that respond robustly to resonances caused by aerodynamic excitation.

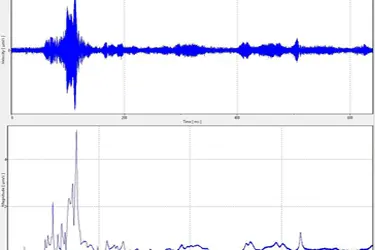

Laser sensors for fast and reliable resonance measurement
Related products

VibroScan QTec Xtra
VibroScan QTec Xtraは、振動を非接触、全視野、前例のない精度で測定する新しいソリューションです。画期的なマルチパス干渉計を備えたQTec® は、光学感度と干渉耐性の点で新しいスタンダードを確立しました。赤外線 (SWIR) レーザーをベースとするXtra は、最高の光学感度を特徴としており、要求の厳しい技術的表面でも高精度の測定を保証します。VibroScan QTec Xtraは、最大32MHzの信号発生器を内蔵しつつも、統合されたデータ取得により最大限の携帯性を保証します。

ポータブルレーザドップラ振動計 VibroGo
VibroGo® は、現場での調査や、機械や設備の状態を素早く簡単にモニタリングするための、バッテリ駆動のポータブルなデジタル振動計です。VibroGo® は、最大320 kHzの広い周波数範囲の振動変位、速度、加速度を、最大 30 m の安全な距離から非接触で測定できます。オンボードでのデータ記録、ライブモニタリング、測定データの迅速な分析機能を搭載することで、VibroGo®はこれまで以上に現場完結に特化したレーザドップラ振動計になりました。

レーザドップラ振動計 IVS-500
レーザドップラ振動計 IVS-500は、品質管理の用途に最適な非接触振動計です。測定周波数帯域は最大100 kHzであり、インライン製品検査やEOL試験に最適で、すばやく高精度な振動音響品質検査や、構造物に起因するノイズ分析、信頼性の高い合否判定が可能です。堅牢でコンパクトな設計であり、既存のプロセス制御システムに容易に統合でき、アプリケーションに合わせた短時間の測定を実現できます。レーザなので接触式センサに見られるセンサ自身の摩耗がなく、マイクロフォンによる音響検査時に必要な外部音響を遮断するための防音機構も必要ありません。
マイクロシステムアナライザ MSA-600
MSA-600 は、MEMS や微細構造の静的・動的な 3D 特性を測定するオールインワン光学測定ソリュー ションで、最大 8GHz まで対応します。MSA-600は、マイクロシステム開発および品質検査を強化し、市販のプローブステーションに組み込むことにより、ウェーハレベルでのテストも可能にします。

長距離レーザドップラ振動計 VibroFlex Range
VibroFlex Rangeは、屋外対応の最大500mの長距離測定に適したレーザドップラ振動計です。橋梁や建物などの大型構造物、稼働中の機械、生産設備など、振動する構造物の構造ダイナミクスと安定性を、遠隔から非接触で簡便にモニタリングします。測定された固有振動数と変位/たわみは、ヘルスモニタリングやシミュレーションのモデル検証などに使用できます。

ご相談ください
当社のスペシャリストが、お客様のプロジェクトに合わせた測定ソリューションで支援いたします。あるいは、重要な要素の測定をサポートいたします。ぜひ、お気軽にお問い合わせください。