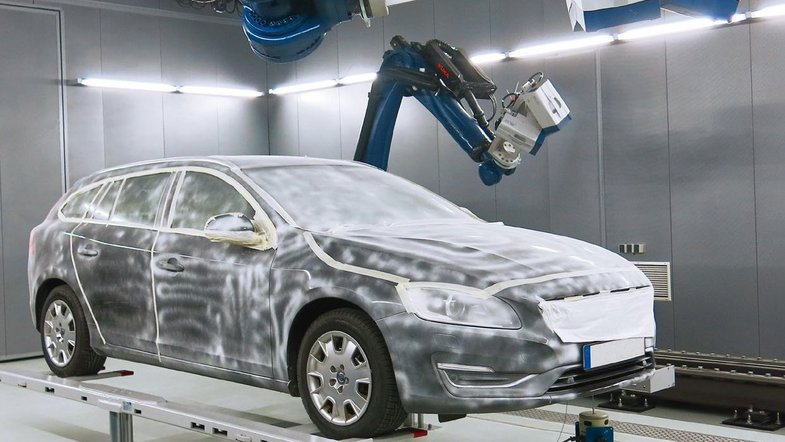
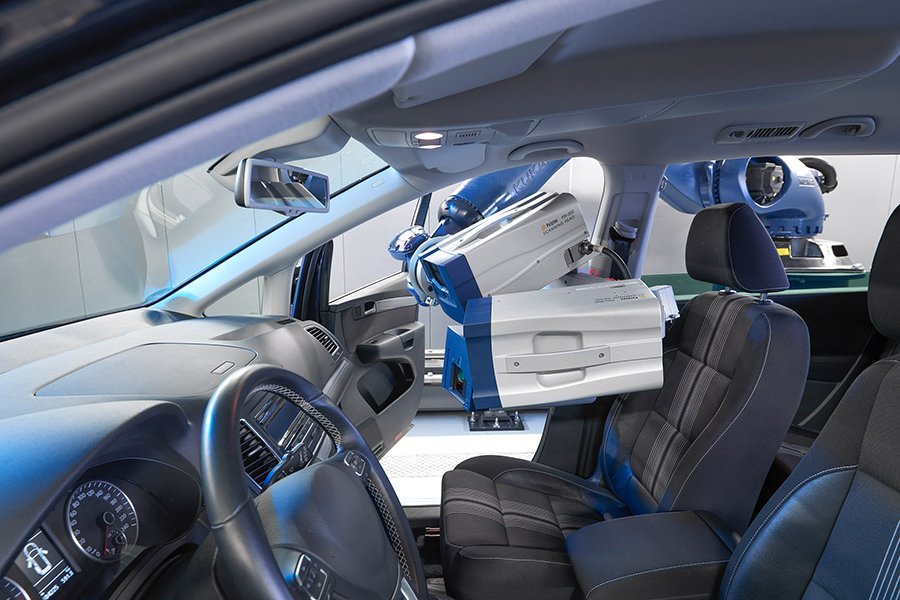
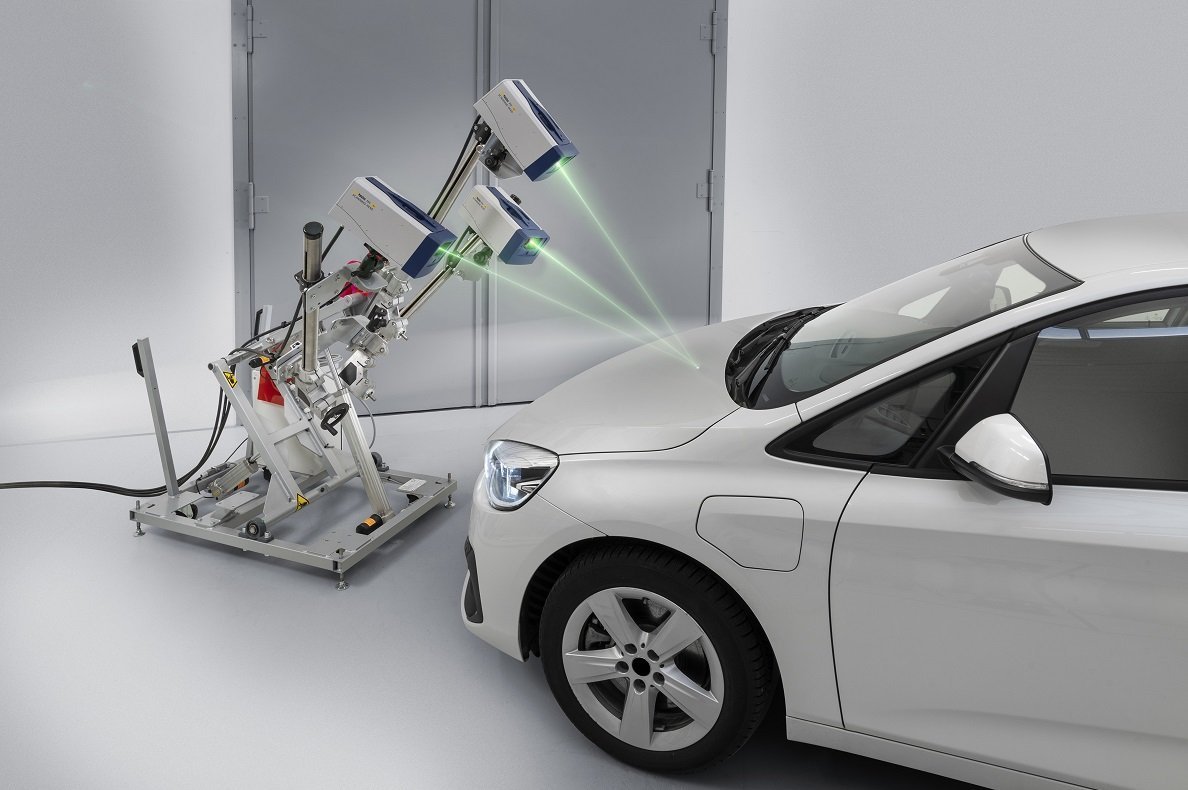
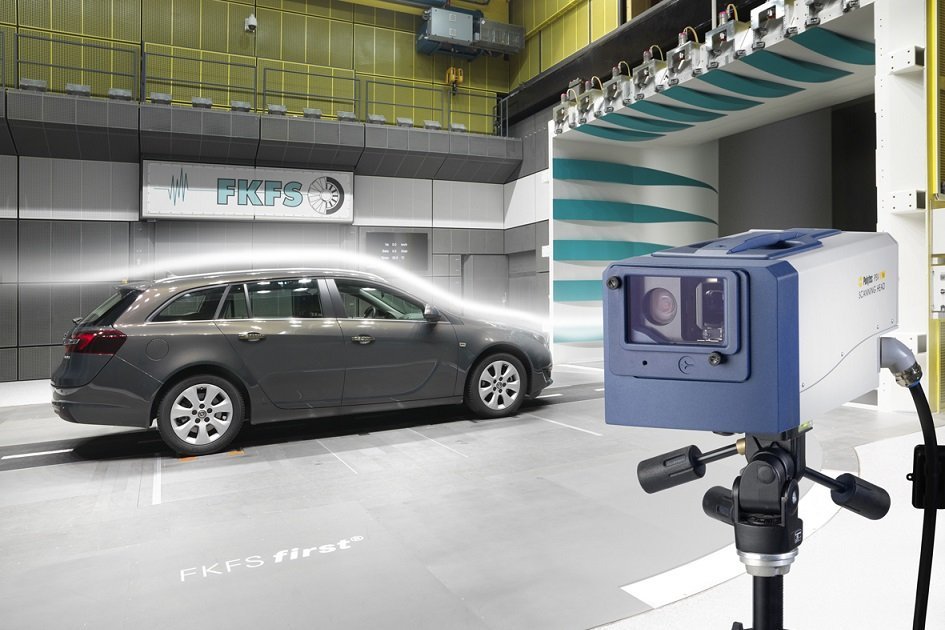
New vibrometer technology in practical testing
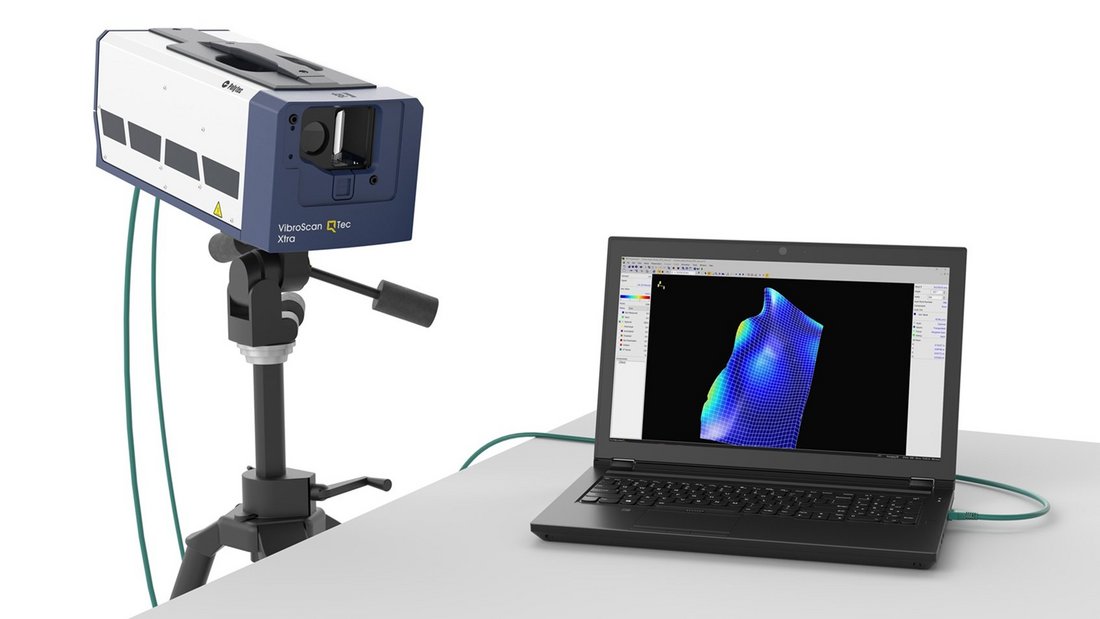
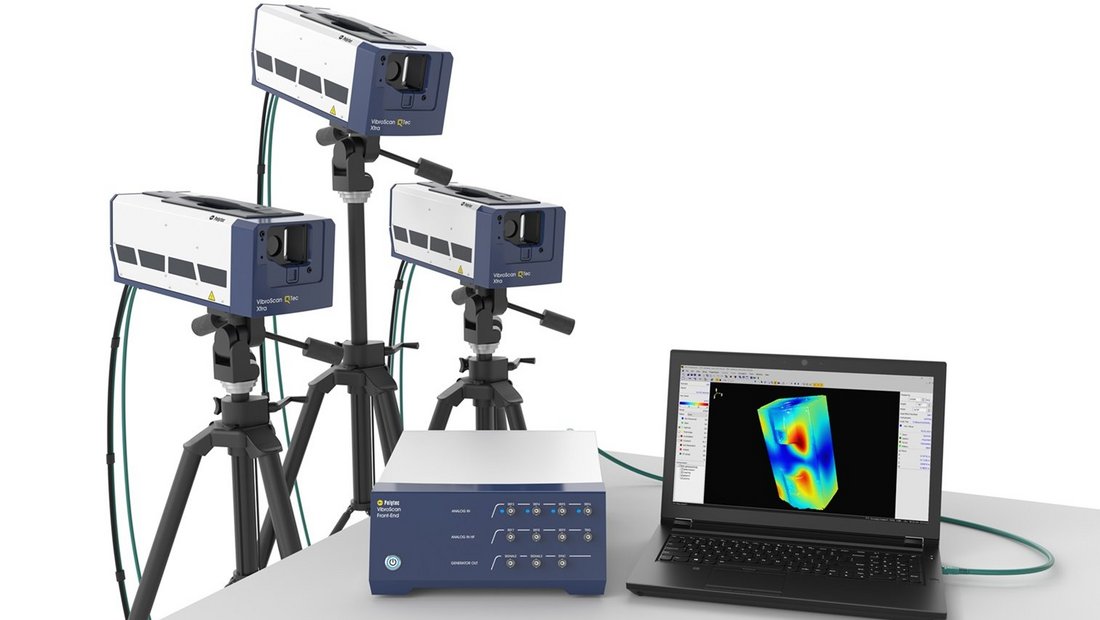
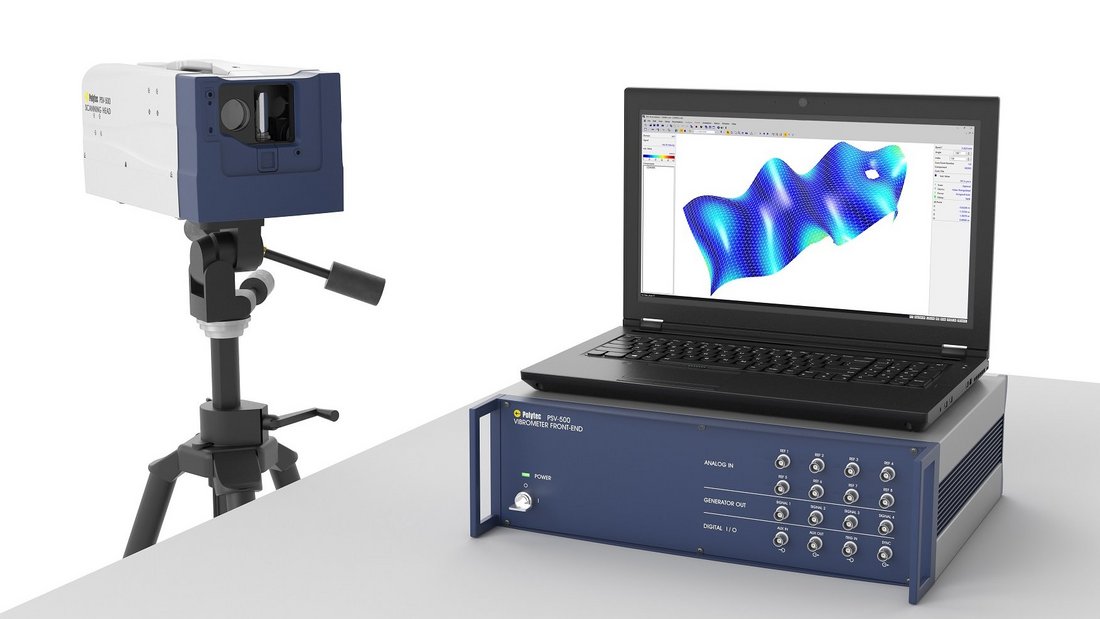
Frequency response function measurement using QTec® multi-path interferometry
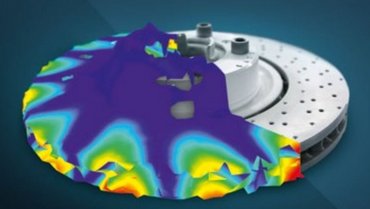
NVH and how to design quiet vehicles
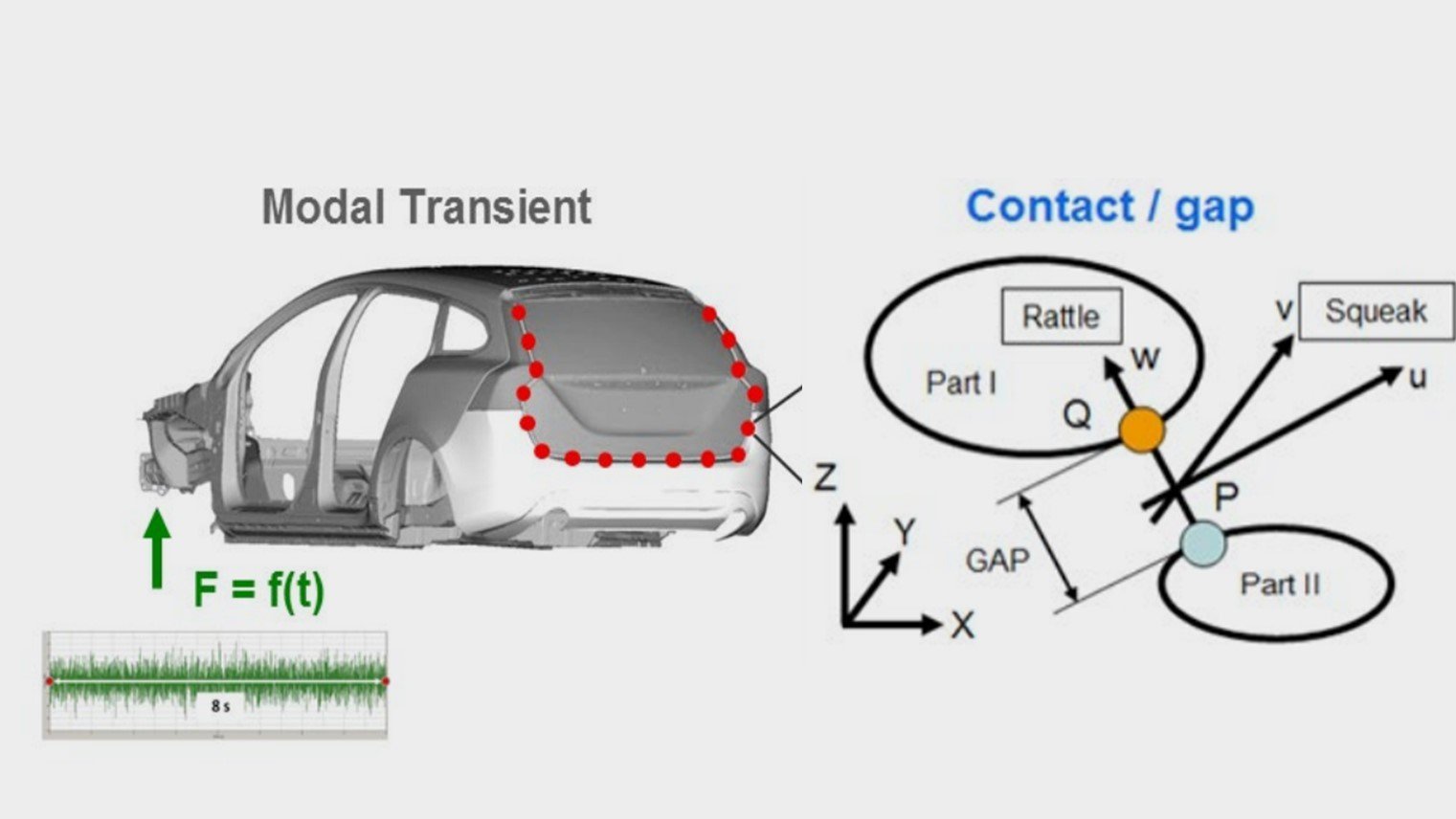
NVH (noise, vibration, harshness) describes the analysis of the influences and sources of noise and vibration behavior in vehicle design and engineering. The objective of NVH analysis or NVH test methods is to optimize noise and acoustics in conjunction with reduced vibration behavior of vehicles and vehicle components. NVH is used for vehicle design, car body design, interior design and more. NVH testing is the crucial basis for reducing unwanted squeaking or rattling noises and thus a quality feature and acoustic signature of any component or complete vehicle.
NVH analysis and non-contact NVH testing?
Describe your NVH test and task
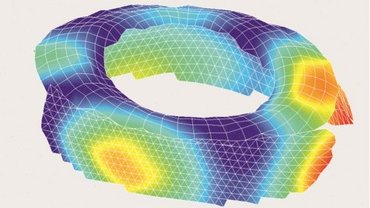
NVH for defined acoustics in door slam testing
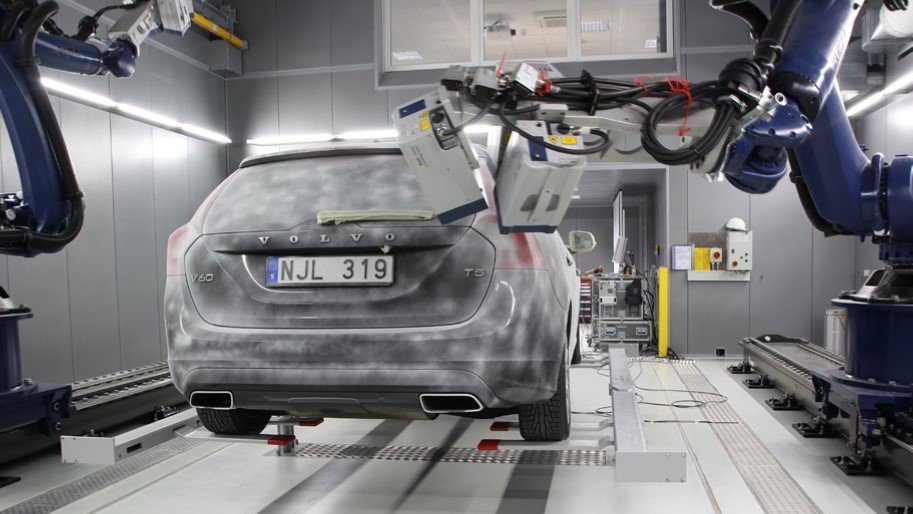
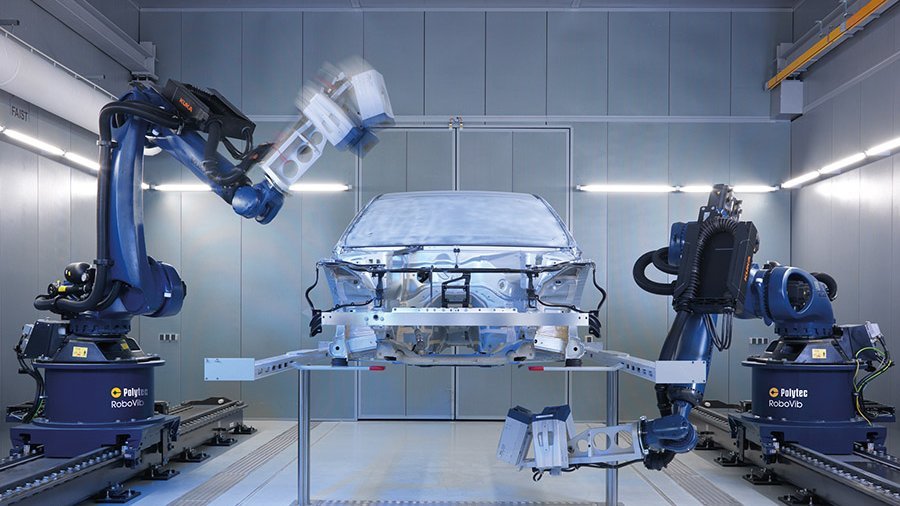
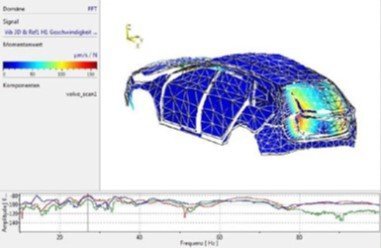
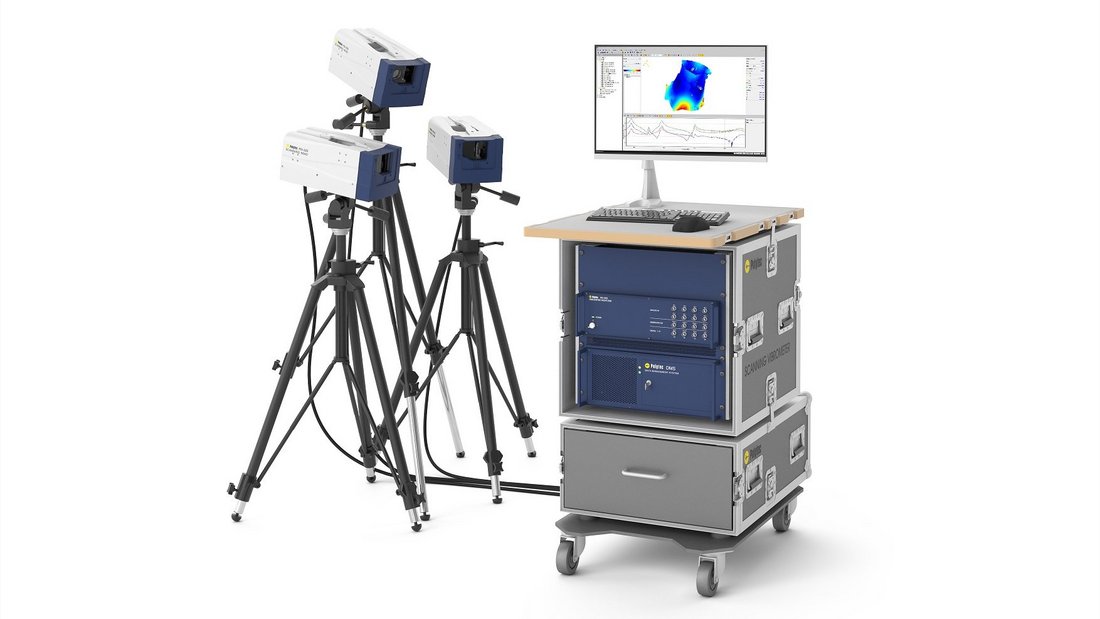
When asking people about their first impression of a new car when entering the passenger cabin, it's either the smell or its sound when closing the door. Thus, the door slam test has become an integral part of NHV analysis for optimizing comfort as well as the perception of quality. In order to measure structural borne noise, using full-field vibration measurement for determining the vibrational velocity in the time domain are of significant value. The Multipoint Vibrometer allows measuring with up to 48 locations synchronously, providing vibration measurement data without any contact or mass-loading influences especially on thin sheet metal panels.